Information system for early detection of threats in the information sphere and forecasting the risks of their occurrence
This document provides a general description of the solutions for designing an information system for early detection of threats in the information sphere and forecasting the risks of their occurrence (IS Vepr) (hereinafter referred to as the System), developed on the basis of contract 0000000009622P000002 No. 2022.132535 dated 22.08.2022.
Content
1 Purpose of the system 4
1.1 Type of activity for automation of which the system is intended 4
1.2 List of automation objects where system 4 is used
1.3 List of functions implemented by the system 4
2 System description 5
2.1 The structure of the system and the purpose of its parts 5
2.2 Information about the NPP as a whole and its parts, necessary to ensure the operation of the system 5
2.3 Description of the functioning of the system and its parts 6
3 Description of the relationship of the AU with other systems 9
3.1 List of systems with which this AS is connected 9
3.2 Description of links between systems 9
3.3 Description of communication rules 10
3.4 Description of the relationship of the AU with the divisions of the automation object 10
4 Description of subsystems 13
4.1 The structure of subsystems and the purpose of its parts 13
4.2 Information about subsystems and their parts necessary to ensure their functioning 17
4.3 Description of the functioning of subsystems and their parts 30
List of accepted abbreviations 34
1 Purpose of the system
1.1 Type of activity for which the system is intended to be automated
Monitoring of information and telecommunication networks and the information space in terms of compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of communications, information technology, mass communications in terms of implementing specialized, thematic monitoring of the media and mass media on the Internet in order to search for and predict potential information threats in various areas of public relations.
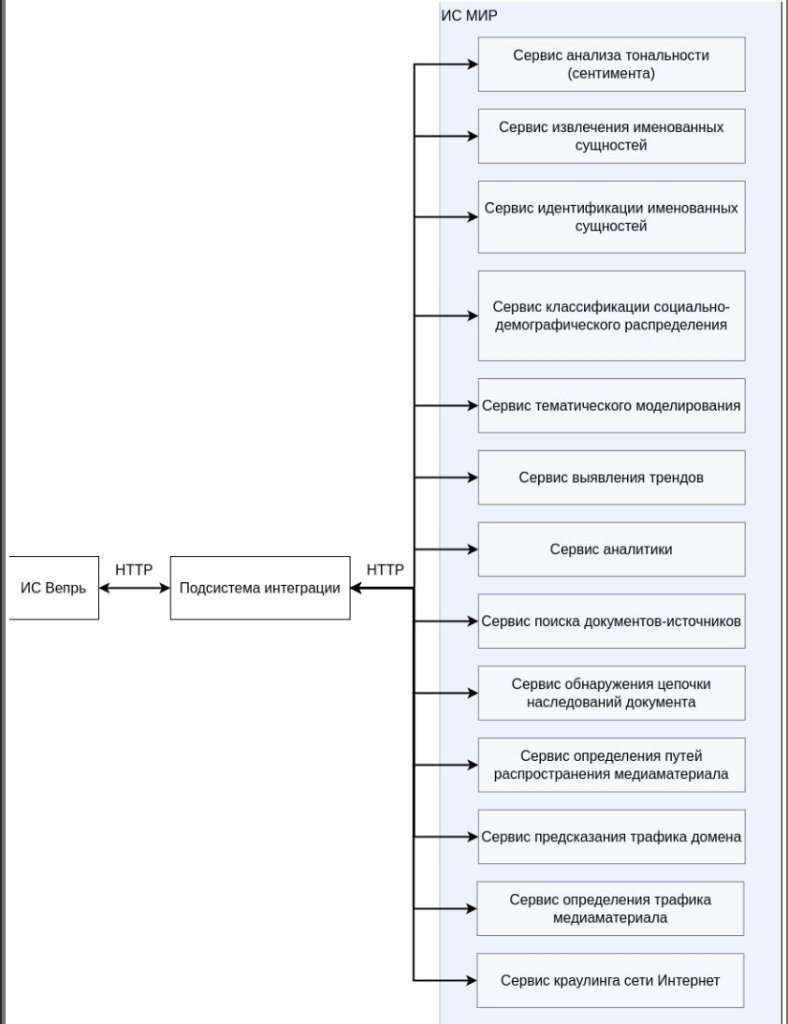
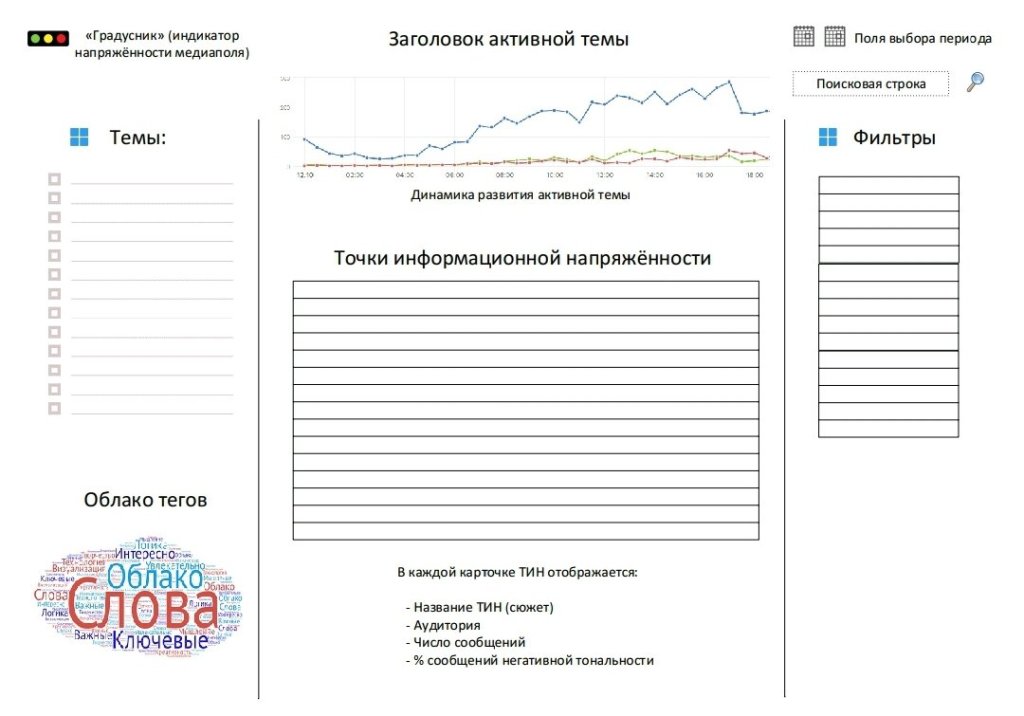
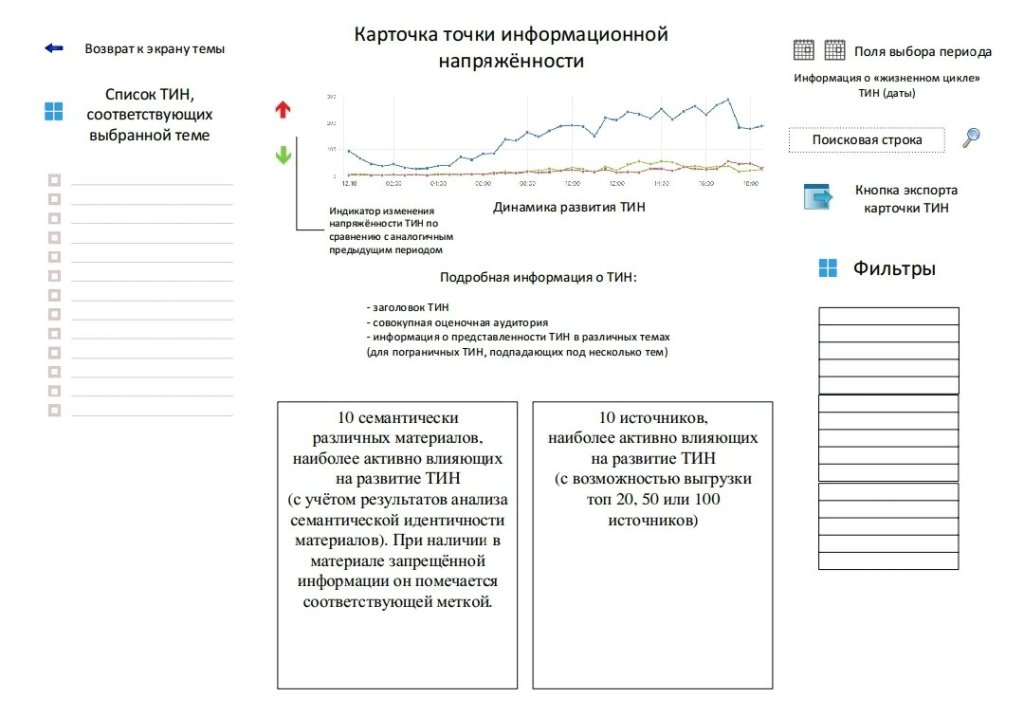

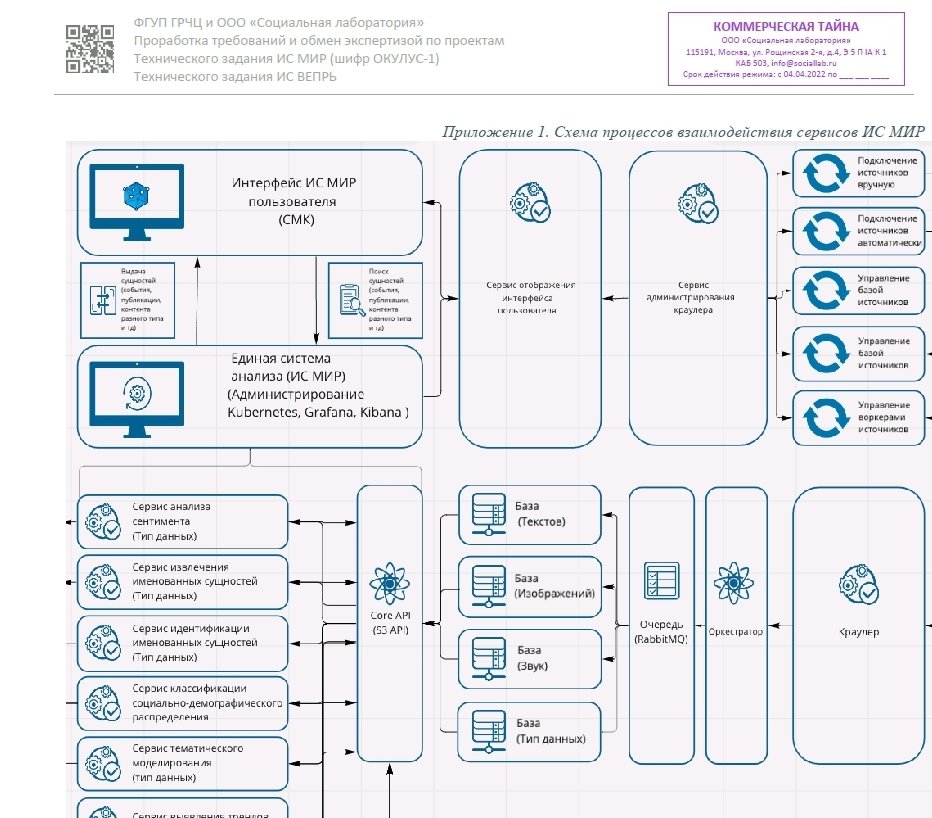
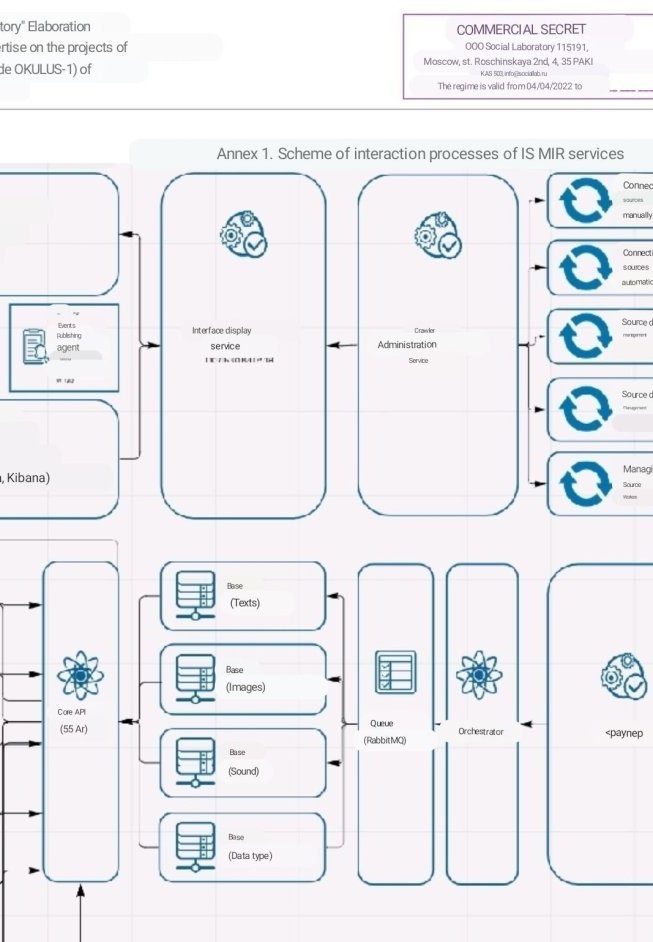
1.2 List of automation objects on which the system is used
The object of automation of the IS “Vepr” is the process of identifying points of information tension in the course of monitoring the information space, which is carried out in accordance with the Federal Law of July 27, 2006 No. 149-FZ “On Information, Information Technologies and Information Protection”.
The system is a tool for monitoring the Internet to identify possible signs of violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation in TIN to calculate potential threats to the individual, society and the state.
1.3 List of functions implemented by the system
The system implements the following list of functions:
− monitoring and analysis of the information field in order to detect points of information tension (ITN), which can be further defined as threats to information security (ISB);
− formation and provision of an evidence base for the presence of TIN;
− formation and provision of an evidence base that can help identify TIN as PEB;
– calculation of ongoing media campaigns on the Internet, carrying potential (with a certain degree of probability) threats, as well as carrying risks of violations of the legislation of the Russian Federation;
− forecasting the risks of the spread of TIN and PEB within the information field (with a certain degree of probability).
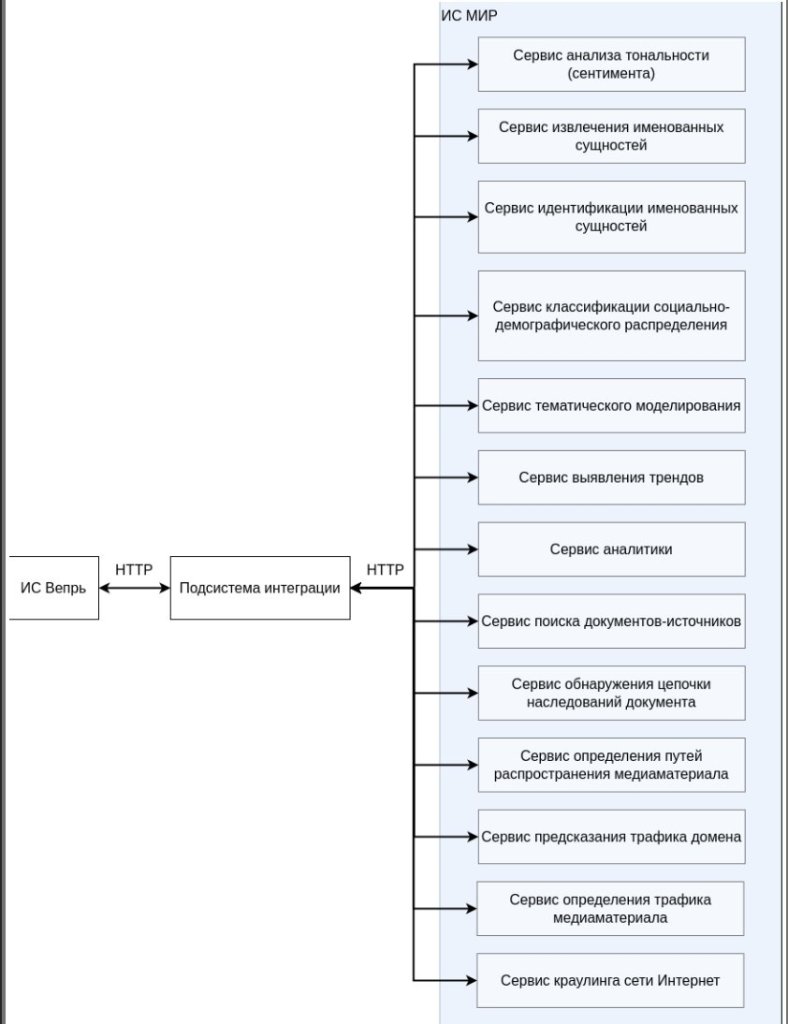
3.3 Description of communication rules
Information exchange between subsystems and services of the Vepr IS, as well as with external systems, is carried out using the TCP/IP multilevel interaction protocol system.
For each subsystem, there is a set of endpoints that allow a request to be passed to the subsystem.
3.4 Description of the relationship of the AU with the divisions of the automation object
To identify threats based on named queries, taking into account the existing model of media clustering by TIN and the available proven evidence base, there is a TIN monitoring service that operates according to the following algorithm:
1. Get media materials that have passed all analysis services as input to the algorithm.
2. Get an estimate of the replication of media materials.
3. Get the tone of media materials.
4. If the assessment of the replication of media materials is more than 1 million in federal sources, and for 20% of media materials a negative tone was determined, then define media materials as TIN.
5. If the assessment of the replication of media materials is more than 1 million in federal sources, and for 8% -19% of media materials a negative tone was determined, then it is necessary to assess the polarization of media materials.
6. If the assessment of the replication of media materials is more than 100 thousand in regional sources, and for 20% of media materials a negative tone was determined, then define media materials as TIN.
7. If the assessment of the replication of media materials is more than 100 thousand in regional sources, and for 8% -19% of media materials a negative tone was determined, then it is necessary to assess the polarization of media materials.
8. If the assessment of the replication of media materials is more than 10 thousand in district sources, and for 20% of media materials a negative tone was determined, then define media materials as TIN.
9. If the assessment of the replication of media materials is more than 10 thousand in district sources, and for 8% -19% of media materials a negative tone was determined, then it is necessary to assess the polarization of media materials.
10. If the polarization assessment revealed more than one polarity and their tonality is opposite, then determine such media materials as TIN, otherwise the media materials are not TIN.
List of functions of the identity and access management subsystem:
Unified (centralized) management of user access to information resources, confidential corporate data.
Creation of user accounts (identifiers).
Management of data for authentication and rights for access to information resources.
In general, the work of the audit subsystem is reduced to registering a certain set of actions for audit purposes:
– actions to create, read, update or delete;
network connection activation;
User authentication and authorization for actions such as user login and logout, failed login attempt with a privileged account (including system administrator or database administrator), or privileged account password reset/authentication requests;
granting, changing or revoking access rights, including adding a new user or group, changing user privilege levels, changing file permissions, changing database object permissions, changing firewall rules, and changing a user’s password;
system, network or service configuration changes, including the installation of software patches and updates or other changes to installed software;
start, end or restart of the application process;
application process interruption, failure or crash, especially due to resource exhaustion or reaching a resource limit or threshold (for example, for processor, memory, network connections, network bandwidth, disk space or other resources) and/or failure of network services, such as DHCP or DNS, or hardware failure;
detection of suspicious/malicious activity, for example, using an intrusion detection or prevention system (IDS/IPS), anti-malware or spyware.
According to the functional requirements, the following types of information security measures are provided:
Protection against unauthorized access;
Firewall and intrusion detection (computer attacks);
Cryptographic protection;
Security analysis;
Monitoring of information security events;
Protection of communication channels.




You must be logged in to post a comment.